- Home
- Top Superfoods
- Aloe Vera
Aloe Vera Benefits as a Nutritious Dietary Superfood

Aloe vera (Aloe barbadensis) is a succulent plant that is cultivated all over the world for its thick gelatinous leaves. When the leaves are cut, a clear viscous substance can be pressed or filleted out of the aloe leaf.
This material is the healing and therapeutic element of the plant that is a rich source of polysaccharides and many other ingredients including lignins, saponins, salicylic acid, vitamins, minerals, amino acids, enzymes and fatty acids.
Aloe is well known commercially for its topical use in the cosmetic
industry in hair and skin products. But, it is also a very popular
ingredient in a wide range of health food products and beverages due to
its number of nutritional components.
Today, many people are also using
fresh raw aloe leaf by "filleting" out the inner gel and consuming it
like a vegetable blended into juice, water or drinks. In fact, whole fresh leaves can sometimes be found in the produce section of many health food markets.
Aloe is about 99% water and is a very hydrating and super nourishing
food for the body. In addition, it contains beneficial phytochemicals
such as anthraquinones and various glucomannans.
It is an excellent top superfood, not only for the skin (even when used internally), but for many systems of the body, helping to boost immunity, purify the liver and aid digestion.
Visit our aloe gel versus aloe juice page for more info on specific differences.
Throughout history aloe was regarded as a virtual panacea for many health conditions and has been used extensively since Biblical times by the Egyptians, the Chinese and different Mediterranean civilizations.
The name "aloe" is thought to have originated from the Arabic word "alloeh" which translates as "shining bitter substance." In Latin the name "vera" means "true." In Ayurvedic medicine it is sometimes referred to as "kathalai" and was mentioned in ancient Indian texts for its properties as an antiparasitic, skin healer and as a rejuvenative plant for the liver and reproductive systems.
Here on this page, we will discuss some of aloe's attributes as a dietary supplement and certain elements of the gel that make it a superhealthy addition to most any blended drink.
What is Aloe Vera?

There are many different types of aloe, from the Aloe genus, growing all over the world in dry and subtropical locations, but the original wild version is suspected to have come from desert regions of Africa and possibly the Arabian Peninsula.
Chiefly, the one used most commonly for medicinal purposes is from the "Aloe vera" species is the Aloe barbadensis, or also called Aloe barbadensis Miller. It is an extremely hardy succulent that can go for long periods of time without water, with developed storage techniques that capture water within its matrix of unique long-chain polysaccharides. Because of these characteristics, the aloe plant can grow in a variety of climatic conditions, most prolifically in zones 8 -11.
The Aloe barbadensis species is said to be the most medicinal of all the varieties. Although, we believe and have personally experienced other species (particularly some growing on the coast of California), that seem to possess strong therapeutic qualities.
There are quite a few aloe hybrids that are used for ornamental and landscape purposes which are likely not as effective as most do not have the stabilized gel in the center of the leaf, which is necessary for the aloe plant's mentioned health benefits.
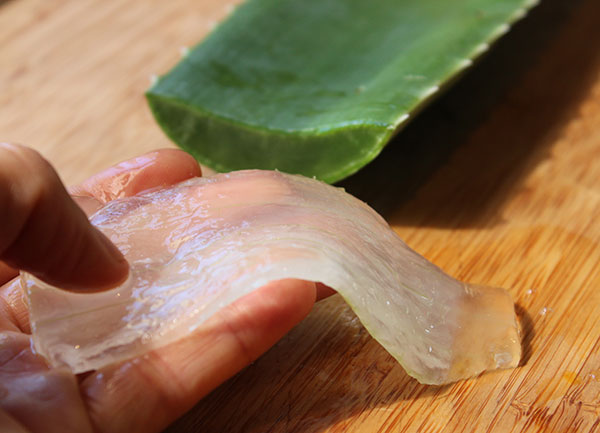

Aloe Vera Benefits
Soothing Digestive Aid and Natural Laxative
There are many foods and herbs that have laxative effects on the digestive system, ranging from mild to more intense in nature.
They can be particularly useful when you find yourself a bit backed up in the bowel movement department and a good way to find relief from constipation without having to use harsh over the counter drugs or other medications.
Consuming aloe vera juice, gel or powder is considered to be a gentle
and mild laxative that also helps to sooth, hydrate and nourish the intestines
and can be an especially valuable food for alleviating and healing
conditions such as colitis, ulcers, IBS, acid reflux and diverticulitis.
We believe that a properly functioning digestive tract, free from obstructions, is the foundation for optimum health and wellness.
This is the system that breaks down the nutrients and
life-force from the food we consume, providing energy to all the bodily
systems. Remember, you aren't what you eat, you are what you digest and assimilate!
Rich in Glucomannans and Anthraquinones

Aloe is rich in glucomannans, a water-soluble polysaccharide that is also a source of dietary fiber and is mainly found in the gel portion of the leaf. It acts as a food thickener and emulsifying agent when blended, much the same way that chia seeds and seaweeds thicken foods, desserts and drinks. The glucomannan constituents in aloe contribute to its laxative effects.
There are also a number of anthraquinone compounds in the leaf that also have cathartic effects. Notably one of them is aloin, which we will discuss further on this page.
Aloin is a bitter latex-like material that, in small amounts, can be helpful for the digestive system and is known to stimulate mucus secretions and increase intestinal peristalsis.
Other anthraquinones, like emodin, are also interestingly found in other purgatives like senna, rhubarb and cascara sagrada, which exhibit similar bowel-stimulating properties. Aloe's emodin content is found in the gel as well as the sap and leaves.
Aloe Helps in Detoxification and Weight Loss
Aloe's digestion enhancing and bowel normalizing effects also help to detoxify the body and can assist in the elimination of undigested waste material as well as toxins. For this reason, aloe is often promoted as an effective supplementary addition to the diet for those wanting to lose excess body weight.
Increases Healthy Micro-Flora and Alkalizes the Body
Mannose is another anti-fungal type polysaccharide nutrient found in aloe gel that can be useful for eradicating unfriendly yeast overgrowth in the colon. Additionally, aloe acts as a prebiotic which helps the proliferation of other friendly micro-flora and probiotic organisms present in the gut. The polysaccharides in aloe vera gel are also beneficial for providing a protective mucous lining in the digestive tract.
Aloe vera benefits also assist in balancing body pH, providing a more alkaline environment which can be helpful for discouraging acidic-thriving gut microbiota. It is thus a great superfood for those with candida (*) and helps to counteract the effects of a diet high in animal-based proteins that can often lead to an overly acidic system. Aloe can also be very soothing for associated conditions such as indigestion and heartburn.
Polysaccharides that Help Boost the Immune System
Used internally aloe vera can be very beneficial for maintaining a healthy immune system. This is due to a number of easily digested mannose polysaccharides or long chain sugars like the glucomannans that appear in the bloodstream where they offer immune-regulating actions.
One particular polysaccharide, called acemannan, stimulates the production of macrophages, a type of white blood cell that plays a significant role in immune response. Acemannan is known to produce immune helpers like interleukin and interferon which can inhibit viruses, parasites, bacteria and fungus.
Polysaccharides are also rich in other superfoods like noni and a number of medicinal mushrooms. And like the mushrooms: chaga, reishi and coriolus, aloe vera is considered an immune building adaptogen as it activates immune defense and adaptive mechanisms that make it easier to deal with physical, environmental or emotional stress in our daily lives.
Aloe stimulates the liver to produce more glutathione, a master antioxidant and detoxifying substance.

Potent Antiviral, Antibacterial, Antiseptic and Anti-Inflammatory
Aloe vera is an antiviral, antibacterial, analgesic, antifungal, antiparasitic and antiseptic agent composed of various compounds like emodin, saponins, anthraquinones, fatty acids, sulfur, salicylic acid and phenols which are substances that provide antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory activity when used both externally as well as internally.
Consuming the gel, powder or juice has been proven in scientific research to be very helpful for its effects as an anti-inflammatory for related conditions like arthritis, ulcers and the inflammatory response associated with cardiovascular diseases.
One study
in the Journal of Ethnopharmacology states, "These results demonstrated
that the extracts of aloe vera gel have anti-inflammatory activity and
suggested its inhibitory action on the arachidonic acid pathway via
cyclooxygenase." The inhibition of COX (cyclooxygenase) is known to
provide relief from the symptoms of inflammation and pain in the body.
Raw aloe is furthermore a nourishing food for healthy joints, not only because of its effects at reducing inflammation, but also because aloe contains beneficial phytonutrients like sulfur-based MSM, which helps to keep the joints flexible and strong.
Using 100% Raw Fresh Aloe Vs. Pasteurized Products
To receive the maximum health benefits, fresh raw aloe leaf gel and juice is best for highest enzyme levels and nutrient content. All aloe products (gel, juice or powders) are pasteurized, not cold-processed. This technique is legally required to remove potentially harmful bacteria. It is best to go with brands that minimally heat-treat with flash pasteurization methods.
Beautifies and Heals the Skin
Not only does aloe soften and beautify the skin when applied directly,
but aloe also heals from the inside out and positively effects the
health of the skin layer when used internally. Aloe's potential cleansing effects on the liver, can naturally assist in providing this skin clearing influence.
In addition, aloe's high water content, polysaccharides and lignins also
lubricate and moisturize the internal tissues of the body which keep
the skin cells well hydrated. The high MSM-based sulfur content additionally helps to build keratin and collagen, two compounds essential for healthy nails, hair as well as the skin.
Of course, aloe is famous for its use as an external skin treatment for a variety of conditions including eczema, rashes, stings, psoriasis and many other skin disorders. The lignin compounds in the gel provide deep penetrative effects at soothing and healing wounds, itchy dry skin and burns when used topically.

The polysaccharides, anthraquinones, saponins, sulfur as well as gibberellin, a glycolic and growth hormone, all help to improve wound healing, increase collagen synthesis, lessen pain, reduce inflammation, decrease scar tissue and disinfect the affected area.
If you have ever put pure aloe on your face, it is like getting a face lift as you feel it simultaneously moisturize and tighten the skin. It is especially great to use after spending time outdoors in the sun.
Aloe vera gel has been reported to have a protective effect against radiation damage to the skin and was used extensively in Japan by those recovering from radiation exposure after the Hiroshima and Nagasaki atomic bombings.
Aloe is thought to have been the secret to Cleopatra's renowned beauty as she was documented to have applied it directly to her skin on a regular basis.
Vitamins, Minerals and Fatty Acids
Pure aloe gel contains the minerals sulfur, calcium, selenium, magnesium, chromium, copper and zinc as well as vitamins A, C, E and some B vitamins. (It is not a good source of B-12 as some claim.) Raw aloe is rich in living enzymes and is also a source of amino acids and fatty acids.
Concerns About Aloin Toxicity
In recent years there has been some controversy in the health food world about the potential toxicity of a substance called "aloin" or sometimes called "aloe latex", a yellow sap-like material that separates the inner gel portion of the leaf from the green rind outer layer.
Aloin, one of the anthraquinone glycosides in aloe vera, is a naturally occurring yellow pigment that has purgative properties or strong laxative effects on the bowels and helps create softer stools. However, consuming too much aloin over a period of time is not a good idea and has been shown to be too harsh on the digestive system in large amounts.
It is especially concentrated in the Aloe ferox leaf, an African species.
Aloin was used as a common ingredient in over the counter laxative drugs, but was banned in 2002 by the FDA as no longer "generally recognized as safe" (GRAS).
It is important to note that high concentrations of aloin have only been
found in some aloe vera juice products. Aloe vera juice is sometimes produced by
using the whole leaf rather than just the inner gel fillet. The straight gel is known to contain very little aloin and is usually rinsed in water to remove it.
However, because of these health concerns, there are now health and safety standards set by the International Aloe Science Council (IASC) that verify and test aloe products and provide the IASC seal of approval on the label.
Some aloe products filter their aloe juice using a charcoal and diatomaceous earth filtration process and others simply use the inner fillet and remove any remaining aloin to meet the required limit for health and safety standards.
Our Thoughts About Aloin
We believe some aloin content can be favorable, as long as you don't over consume it for long periods of time. It has a bitter taste that in some cases can be quite beneficial to the digestive tract.
It is also significant to remember that plant-derived remedies containing aloin and other "anthraquinones" have been used medicinally for centuries by many cultures around the world.
When filleting fresh aloe leaf, you can skip the rinsing stage if you prefer to have more bitter aloin content for medicinal purposes.
How to Fillet Fresh Aloe and Remove the Aloin
Fresh aloe is a superior choice for consumption in drinks and smoothies. Whether you buy fresh aloe leaves or grow your own you will need to know "how to fillet" your leaves.
(Visit our page on more specifics on how to fillet aloe.)
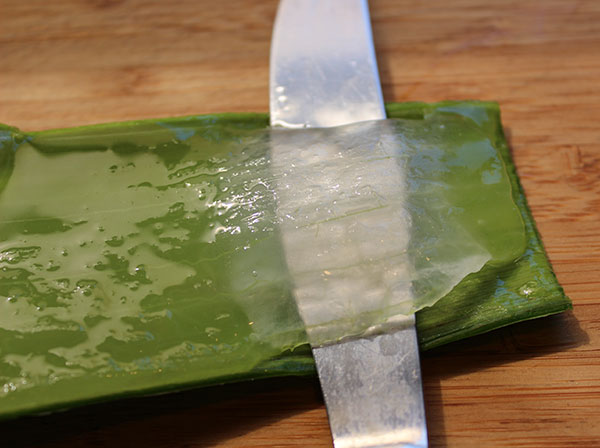

- Take your whole leaf and cut off the top and bottom with a pair of kitchen scissors.
- Next, cut off along the vertical pointy edges on both sides. Now you are ready to fillet out the clear inner gel.
- Hold your leaf down on a chopping board and use a knife to slice just above the green layer, continue all the way to the end of your leaf.
- Next, turn your leaf over with the gel side exposed and repeat the previous step.
- Now you will have a whole thick gelatinous piece which you can soak in pure water to remove any possible aloin. Aloin is easy to see as it is yellow and will usually turn your water yellow if it is present.

Types of Aloe
We always suggest using pure raw aloe vera products that are not high heat pasteurized. In addition, it is good to make sure your aloe does not contain other ingredients, fillers or fragrances that are common when using it for topical treatment.
- Aloe Gel - This is the material in the center of the leaf that is cold pressed into a translucent thick pourable gel.
- Aloe Juice - Most pure aloe juice is made using the entire leaf and then filtered to remove the aloin content.
- Aloe Powder - This is the whole leaf, with some aloin removed, dried into a powder form. Some powders use Aloe ferox, an African species with more potent purgative effects and bitter aloin components.
- Fresh Aloe Leaf Fillet - This is the filleted thick gelatinous portion of the leaf center.
How to Use
Aloe vera can be considered both a "medicine" and a "food." We enjoy the fresh gel in smoothies and blended drinks, particularly in the hot summer months as it is refreshing and cooling to the body.
It is also
appropriate to use when doing a juice fast or cleanse to help promote
the detoxification process. It is additionally beneficial when using zeolite or activated charcoal to prevent constipation that sometimes results from using these supplements.
Aloe doesn't have a strong flavor and is easy to blend into most recipes and beverages. We always recommend using high quality 100% pure, raw, organic aloe vera gel, powder or juice for the greatest health benefits.
Also see our goji berry lemonade and charcoal lemonade recipes.
And, of course, the best aloe is "fresh aloe" that is filleted and soaked to remove most of the aloin content. You can purchase fresh organic aloe leaves online from many quality distributors.
For an easy nutritious energy drink blend coconut water, blue green algae powder, Vitamineral Green and aloe vera gel in a blender, serve in a cocktail glass.
Precautions:
Some people with sensitive skin get an immediate but temporary redness and sometimes a burning sensation after using pure aloe gel topically. Excessive internal use may cause abdominal cramping and loose stools. Avoid consuming aloe vera when pregnant or breastfeeding. Consult your physician or health care provider before using aloe if you have a serious medical condition or are taking prescription medications.
Shop Related Products (About Affiliates & Amazon Associate Paid Links)
Affiliate Disclaimer: This section contains affiliate product links. If you make a purchase through our recommended links, we receive a small commission at no additional cost to you. Thanks for the support.