- Home
- Nuts and Seeds
- Cacao Beans
Cacao Beans, Nature's Raw Chocolate

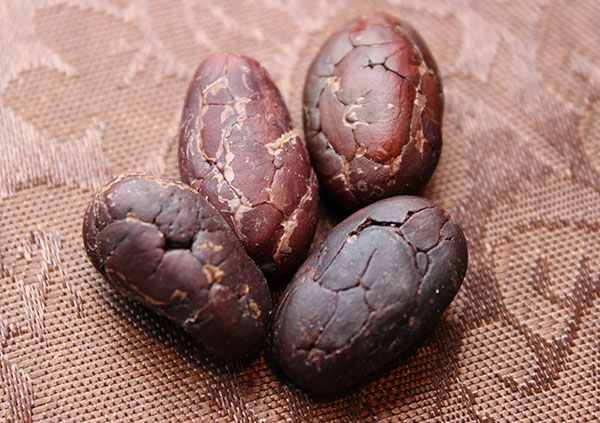
Raw cacao beans are the seeds or "nuts" of the cacao tree, an evergreen native to tropical forest regions of Central and South America as well as Mexico. All chocolate in existence comes from the cacao bean and the genus Theobroma of which there are over 20 different tree species.
Although cacao has been used for thousands of years by ancient peoples, it has only just recently been reintroduced to the world in the last decade as a natural unprocessed form of "raw chocolate." This version, which is very different than the chocolate most people are familiar with, is a super rich source of antioxidants, bitter alkaloids and other energy enhancing phytonutrients.
Cacao, pronounced "ka-kow", was specifically popularized in the early 2,000's by health advocate and raw vegan pioneer, David Wolfe. It is really due to his research and involvement with the cacao bean that has sparked a renewed mainstream interest in traditional ways to prepare, consume and enjoy this amazing superfood.
Because of raw chocolate’s low temperature fermentation, drying and processing techniques, many more nutritional components are made available, providing for higher levels of immune boosting antioxidants but also mood elevating neurotransmitters like anandamine, serotonin, and phenylethylamine (PEA).
For a majority of people who enjoy eating chocolate on a regular basis, cacao can be many steps up from the average chocolate bar and a much better option over highly heated or sweetened milk varieties often made with extremely refined low-grade cocoa liquor.
For others, raw cacao is best used in moderation, in small amounts, and reserved for special occasions in dessert recipes or elixir-type drinks combined with other foods and superfoods.
History of Use
Cacao was traditionally consumed in ancient times for ceremonial or medicinal purposes as a frothy beverage which also included other ingredients like chili, honey, maize and vanilla.
Cacao beans were a highly revered food in the ancient Mayan, Olmec and Aztec civilizations, where they were used in sacred ceremonies and as a form of monetary exchange. Cacao pod depictions are found all over the art and pottery of these cultures with archeological evidence from these regions dating back somewhere between 1400 and 1500 BC.
After the Spanish conquest, cacao was introduced to Europe by the Spaniards, who also brought cacao cuttings to other parts of the world, including the Philippines and the West Indies. It is speculated to have spread to Africa and other parts of Asia via European traders. Today, 80% of the global cacao market is produced mostly in Africa as well as Indonesia, far from its original homelands.
What is Cacao?
Cacao beans come from the main species of cacao, Theobroma cacao, a shade tolerant rainforest tree that grows about 12-16 feet tall under the canopy of other tree species. Throughout the year it produces small flowers right off the trunk that later form cacao pods, elongated oval-shaped shells about 6-12 inches long. When the pods are mature they hold between 20-60 beans nestled inside a layer of white soft cacao fruit.
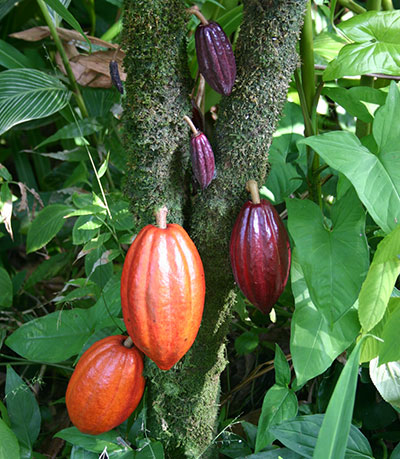

There are over 10 different main groups of cacao bean varieties that vary considerably in quality and flavor. The three main ones often referred to are the Criollo, Forastero and Trinitario. Most chocolate is made from the Forastero bean because it is easy to grow and cultivate for mass production, but it is substantially lower in quality, flavor and nutritional components. Trinitario is a cross between Criollo and Forastero.
Criollo is one of the most valued because it is a genetic descendant of very old cacao trees. Criollo trees have very deep roots, uptake a high amount of nutrients and have a complex aroma and taste. Most high quality organic cacao beans are the Criollo variety from Peru. Another famous heirloom, however, is the Arriba Nacional, which is specific to Ecuador.

How are Cacao Beans Processed?
Cacao beans are not edible right off the tree but must be fermented to break down amino acids and enhance flavor as well as color. Right out of the pod, they are enmeshed in a white sweet fruit pulp and are traditionally piled in heaps and covered. This is when beneficial microbes naturally present on the beans initiate the fermentation process.
Raw cacao is typically fermented within the cacao fruit pulp for several days to "sweat" and to remove excessive bitterness. The fermented beans are then sun-dried on screens, not reaching temperatures above 118-120°F.
The skins are usually removed to make raw cacao nibs (crushed up peeled cacao beans), cacao paste, cacao powder and cacao butter.
Cacao Vs. Cocoa
For more on the differences between cacao and cocoa, visit our cacao vs cocoa page.
Both cacao and cocoa originate from the cacao bean, but cocoa is basically a roasted version of raw cacao that is usually sold as a cocoa powder or cocoa liquor. Cocoa is traditionally what is blended with other ingredients to make chocolate bars.
Unprocessed beans or cacao nibs are the product of 100% pure raw
chocolate in its whole complete state. The words cacao and cocoa, however, are often
used interchangeably these days in the food industry for
marketing purposes.
Purchasing Organic Fair Trade
It is very important to always avoid any chocolate products coming from West Africa, especially the Ivory Coast and parts of Ghana. Cacao plantations in these regions have been flagged by the International Labor Organization for providing extremely unhealthy work conditions in addition to implementing the inhumane use of young children in their farming practices.
It is therefore important to purchase from companies who are certified Fair Trade or are grown in a sustainable manner by local cacao producing communities.
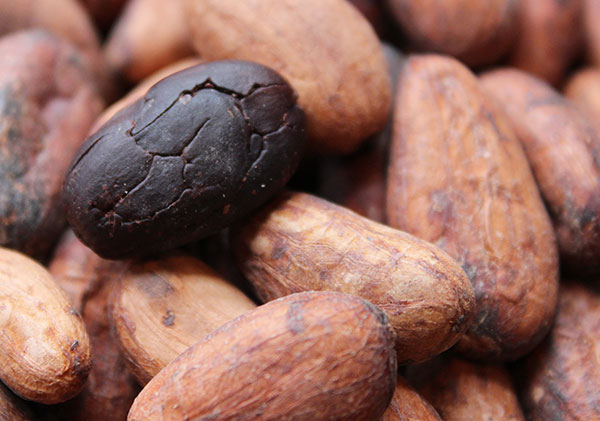

Cacao Beans and Theobromine Content
Does Cacao Contain Caffeine?
Cacao actually contains very little caffeine. The active ingredient in raw chocolate that acts like a plant stimulant is theobromine. Theobromine is a bitter alkaloid and is distantly related to caffeine, but they are not the same substance.
Theobromine and caffeine are both xanthine
alkaloids and bronchodilators, which help to dilate the blood and open
the lungs. Even though cacao is not a nervous system stimulant per say, it can powerfully activate the cardiovascular system, which can have similar effects to caffeine for some individuals.
By volume, cacao nibs or beans contain only about 0.88 to 2.34% theobromine and 0.05 to 0.36% caffeine, with the amount increasing when cacao is concentrated as a powder, paste or liquor.

Sacred Cacao Use
Mucuna has been used as an ingredient with raw chocolate in the Amazon for over 2,000 years. It adds a nice calming balance to the theobromine or any possible caffeine in cacao.
It is our opinion that cacao is one of those foods that should be used with reverence and respect and not over-consumed or used on a regular basis. Despite its relatively low theobromine and caffeine content, some people can be particularly sensitive, especially if over-eaten. It is often best to reserve it for special occasions or in spiced herbal elixirs as was customary in ancient times. One of the significant benefits of cacao is that its actions help to deliver and activate other superfoods, tonics and medicinal mushrooms.
We ultimately believe life should be fun and eating fun, great tasting foods (within reason) is a part of a balanced, happy life. Most people love the taste of chocolate and raw chocolate is a much healthier upgrade from processed and refined cocoa and cooked chocolate products.
Cacao Health Benefits
Antioxidants in Raw Cacao Beans
Cacao is one of the world's most antioxidant-rich superfoods, containing high amounts of flavanoid and polyphenol content including catechin, epicatechin, procyanidin, anthocyanidin and resveratrol. All foods high in antioxidants are very beneficial to the immune system because they help neutralize and prevent the damaging effects of free radicals in the cells and tissues.
Raw cacao contains a much greater number of antioxidants compared to processed dark chocolate, as antioxidants are degraded when exposed to high heat. In addition, antioxidants in their raw state are significantly more stable and far easier to metabolize.
According to an article published in the New York Times, "Fresh cocoa beans, however, are far richer in flavonol -- about 10,000 milligrams per 100 grams, or about seven tablespoons -- than processed chocolate products." Most processed dark chocolate is commonly concentrated in around 500 milligrams per 100 grams flavonol antioxidants.
Cacao and The Cardiovascular System
The Aztecs referred to cacao as "yollotl eztli", meaning "heart blood" and it is believed to help one take action grounded on heart-based intuitions rather than logic-minded thinking.
Cacao beans and their array of phytonutrients are particularly supportive for cardiovascular health with blood thinning properties helpful for reducing blood clotting and lowering blood pressure. These effects are also thought to be due to the flavanols that boost the production of nitric oxide, which causes the blood vessels to open and relax.
In addition, cacao contains certain compounds that are believed to suppress P-selectin, a molecule that increases inflammation and is associated with arterial thrombosis.
In addition, the antioxidant quercetin also helps to support the cardiovascular system by encouraging blood flow in addition to regulating healthy cholesterol and triglyceride levels. The saturated fat content in cacao butter is primarily from stearic and palmitic acids, are considered be two healthy fats that have neutral effects on cholesterol levels.
Theobromine contains xanthine alkaloids and bronchodilators which help to dilate the blood as well as open the lungs and improve overall circulation. As a magnesium-rich food, cacao beans are also known to improve the flow
of blood and oxygen to the arteries which may additionally assist in
lowering blood pressure levels.
In a 2009 article published in the Journal of Cardiovascular Pharmacology it states that, "A full range of health benefits can today be associated to the actions of flavanols and procyanidins on vascular function. These benefits are mainly ascribed to diets rich in flavanols and procyanidins, and chocolate and cocoa derivatives are among the most valuable components of such a diet."

Contains Mood Elevating Neurotransmitters
Cacao can act as a natural antidepressant, containing a powerful combination of constituents that help to uplift the spirit as well as "open the heart."
Consuming only small quantities of raw chocolate is known to be helpful for brain stimulation and the release certain neurotransmitters, like anandamine, serotonin, and phenylethylamine (PEA), which can activate positive emotions like euphoria.
These characteristics are one of the reasons chocolate is a world renowned aphrodisiac for love and passion.
PEA and Anandamide
The primary components responsible for these mood elevating effects
are the antioxidant compounds phenethylamine (PEA) and anandamide.
PEA is present to a large degree in raw chocolate, as well as blue green algae, but is reduced by high heat temperatures. PEA works in the parts of the brain involved with focus and alertness. It is the natural chemical produced by the body when we "fall in love."
PEA is the molecule behind certain monoamine neurotransmitters such as dopamine, epinephrine (adrenaline) and norepinephrine. Increased levels of PEA in the brain encourage the release of dopamine which naturally invokes pleasure and promotes a positive mental attitude.
Anandamide, also referred to as the "bliss chemical", is a neurotransmitter that is naturally released, like PEA, when we are feeling good and comes from the Sanskrit word "ananda" which means joy, bliss or delight.
Anandamide was discovered as an ingredient present in chocolate in 1996 by neuroscientist Daniele Piomelli, along with two other anandamide inhibitors N-oleoylethanolamine and N-linoleoylethanolamine. These two other compounds actually help anandamide and its bliss provoking sensations to stay in the body for a longer period of time. This is especially the case when using raw cacao beans, powders or nibs rather than cooked and nutritionally degraded chocolate variations.
 Arriba Nacional from Ecuador
Arriba Nacional from EcuadorHigh in Tryptophan
In addition, cacao contains sufficient quantities of the essential amino acid called tryptophan, another mood-enhancing nutrient. Adequate amounts of tryptophan in the diet are extremely important for the production of the neurotransmitters, serotonin and melatonin.
Serotonin is important for proper neurological functioning and helps to protect against the impacts of stress and anxiety. Many people are familiar with melatonin as a necessary ingredient for a restful nights sleep. Tryptophan is highly volatile to high heat temperatures, so it is often lacking in cooked foods or processed chocolate.
Raw Cacao Bean Nutrition
Truly raw cacao is a "whole food" containing a complete and comprehensive matrix of minerals, especially magnesium, iron, manganese, chromium, sulfur as well as healthy fats, fiber, vitamins and many antioxidant-rich substances.
High in Magnesium
Cacao is known to contain one of the highest sources of the
alkaline mineral magnesium. Magnesium is an essential component in the absorption of calcium which helps to provide strong healthy
bones and teeth. Magnesium also helps to
relax the muscles, nerves, reduces pain in the body and is involved in energy production.
It is estimated that 80% of those who eat a SAD diet
are chronically deficient in this mineral with the average American diet containing less than 50% of the U.S. recommended daily allowance for magnesium.
Again, Cacao is Not for Everyone!
People who have
candida or
parasites should dismiss use until these health issues have resolved.
Carob powder can be used as a replacement in desserts for those who like the taste of chocolate, but are sensitive to its potential side-effects.
We have experienced adverse effects from raw cacao, such as
over-stimulation and later irritability, when consumed in large
quantities or not in proper proportions with other foods. In addition, Vata body
types or doshas may be particularly sensitive to raw chocolate and should avoid or eat it in very small
quantities as an occasional treat.
Types of Raw Cacao
1) Raw Cacao Nibs
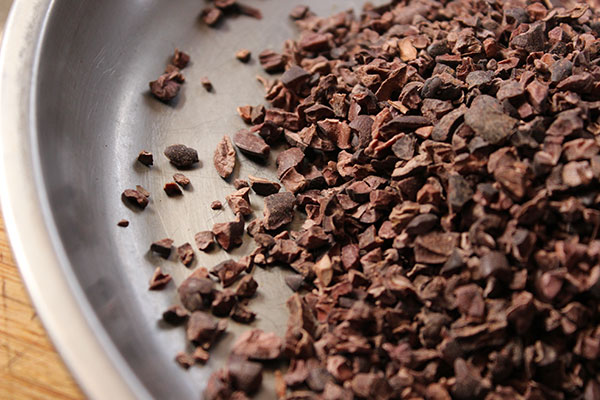

Raw cacao nibs are the little pieces of the peeled cacao bean that have been crushed. They are a more convenient way to use cacao and still maintain freshness as well as nutritional value. The nibs blend up well in shakes and add a crunch to any dessert as a topping or ingredient.
2) Cacao Powder
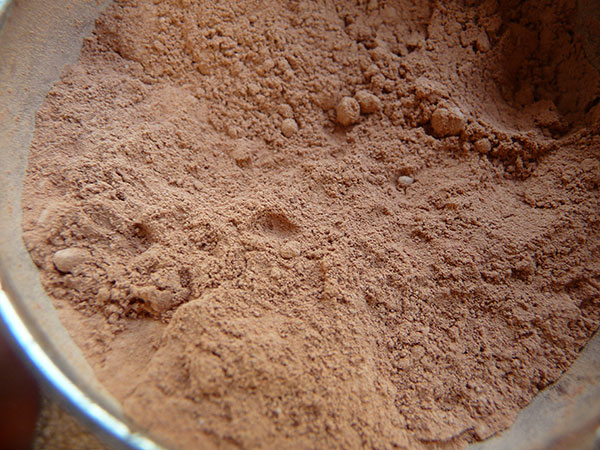

The cacao powder is made by taking the fat and oil content out of the cacao paste and grinding it into a fine powder. Because of this, it is more concentrated in theobromine but lower in calories. Cacao powder has a smoother texture than the ground beans or nibs for making raw chocolate treats.
3) Cacao Paste

Cacao paste is like using baker's chocolate. It is dark, unsweetened and easy to melt at low temperatures and incorporate into recipes. It is essentially the whole peeled cacao bean ground into a paste-like texture and then hardened.
4) Cacao Beans

There are two versions of the cacao bean. One is peeled and one is not. We actually prefer the unpeeled variety for added fiber, enjoying them closer to the way nature intended. The peel also protects the quality of the bean for a longer period of time when stored.
5) Cacao Butter

Cacao butter is the whitish-colored solidified oil that results from pressing ground cacao beans into a paste and extracting all of the fat and oil content. This fat is melted at low temperatures and poured into a mold. When it cools it becomes a solid that is usually sold in chunk-like pieces.
The saturated fat content in cacao butter is primarily stearic and palmitic acids, two healthy fats that have neutral effects on cholesterol levels.
How to Use
Cacao is very beneficial when used with herbs and adaptogens that work to build and replenish the "deep immune" health. Some of these superfoods include the medicinal mushrooms as well as the Chinese tonics and Ayurvedic herbs.
You can soak your beans, either peeled or unpeeled, and blend them up into shakes, chocolate milk and raw desserts of all kinds.
Or used a combination of powder, cacao butter and whole cacao in some of our many cacao recipes, like our chocolate cake or fudge recipe.
Precautions:
Avoid cacao consumption if you have a sensitivity to chocolate which may cause allergic reactions like skin rashes or migraines. Limit use or avoid when pregnant or breastfeeding. It is best not to eat cacao beans if you have candida overgrowth or a parasitic infection.
Shop Related Products (About Affiliates & Amazon Associate Paid Links)
Affiliate Disclaimer: This section contains affiliate product links. If you make a purchase through our recommended links, we receive a small commission at no additional cost to you. Thanks for the support.