- Home
- Super Fruits
- Golden Berry Plant
Golden Berry Plant, Benefits of a South American Superfruit
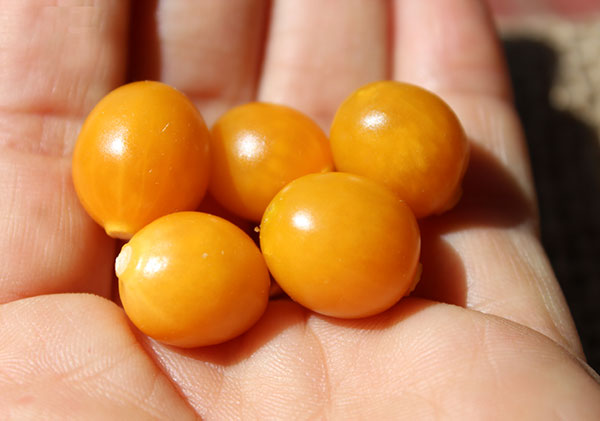

The golden berry plant is a unique South American fruit species native to areas of Peru, Ecuador and Colombia. Producing shiny orange-yellow fruit the size of a marble, golden berries are a now popular dried superfruit known for their higher amounts of antioxidants and other distinct plant compounds.
Also called cape gooseberries, Incan berries or groundcherries, they contain certain carotenoids, withanolides and polyphenols well researched for their immune modulating and anti-inflammatory attributes particularly identified to help inhibit the growth of liver, lung and oral cancers.
Golden berries are a great source of plant-based vitamin C and are another superfruit variety to consider adding to your diet to help increase daily intake.
Like acai, noni, maqui, cranberry, camu and other superior fruits and berries, they are a health enhancing way to dramatically increase your intake of antioxidant-rich phytonutrients and other rare constituents not found in your everyday fruits and produce.
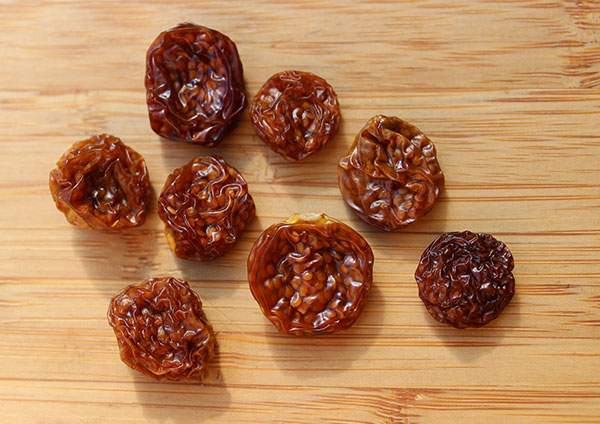
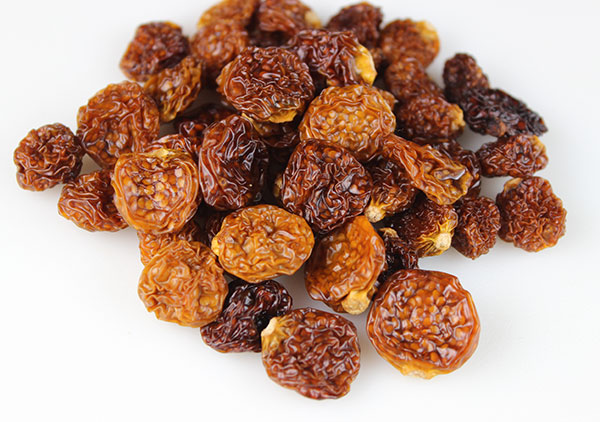
When dried, the berries have a thick wrinkly skin with a chewy interior and a tart mildly sweet flavor, similar to the kumquat fruit. They are a delicious snack food eaten like raisins, or can be incorporated into a number of drinks or desserts, like pies, puddings, lemon bars, jams or fruit tarts.
What are Golden Berries?
Golden berries (Physalis peruviana), are not a true berry, but come from the Solanaceae family of nightshades indigenous to the high-altitude, tropical Andes regions of Colombia, Ecuador and Peru. The berry is also commonly referred to by a number of different names such as Incan berry and pichuberry, for its native habitat locations by Machu Picchu and other acknowledged Incan sites.
It is a known fact that the wild golden berry plant was a utilized food source of the Incan civilization, but to what degree is unclear. The Incas are believed to have been one of the first people to cultivate the plant from its wild origins.
From South America the berry was propagated in England and South Africa in the Cape of Good Hope, where the name cape gooseberry is thought to have originated. Soon after, Physalis peruviana was introduced to England, Australia, New Zealand, and many of the Pacific islands, like Hawaii where it is known as poha. Today it is widely cultivated in tropical, subtropical and even temperate areas, such as India, Thailand, northeastern China and parts of U.S.
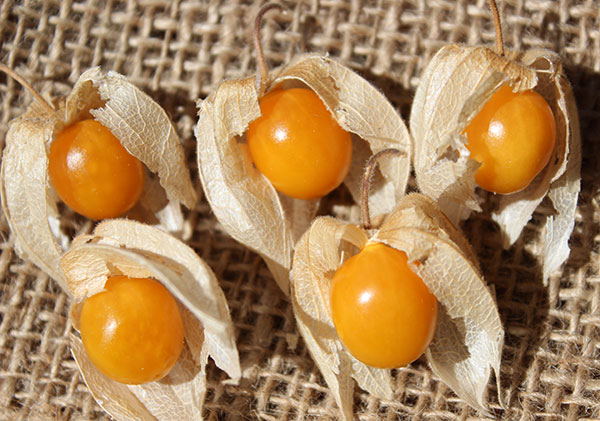
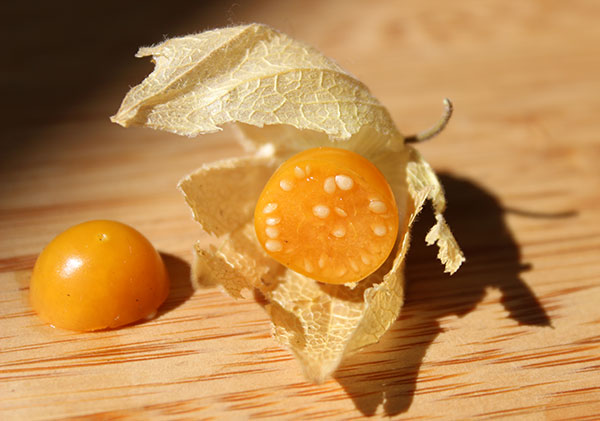


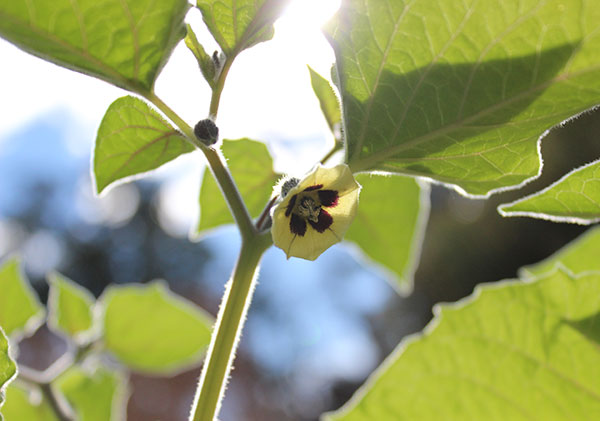
The golden berry is a seasonal perennial fruit that is typically harvested throughout the summer months, producing round orange marble-sized berries, 1/2-3/4 inch (1-2 cm) in diameter, with many tiny edible seeds. The berry grows from the plants light yellow bell-shaped flowers and is enclosed within a unique papery calyx much like that of the tomatillo tomato (Physalis philadelphica) or the Chinese lantern species. This husk protects each individual berry while it matures and is quite decorative in its presentation.
The outer casing is green with dark vertical striations and eventually develops a golden-yellow color when ripe, at which stage it will easily fall off of the plant when touched. After harvesting, the thin sheath will turn a straw color and become somewhat veined and parchment-like over time.
The berries will continue to ripen off the plant and remain fresh within the husk for a shelf life of about 30 days at room temperature. They will then dry like raisins or can be dried immediately after harvest in a food dehydrator. Once it is removed from the calyx it can be consumed raw as a whole berry or used fresh in recipes.
Other parts of the golden berry plant are known to be medicinally useful, including the leaves, stems and roots as well as the berries. However, the leaves and stems are traditionally used for external skin treatments rather than ingested.
Golden berries are grown commercially in regions of Colombia and Peru, where they are dried like raisins and sold for international export.
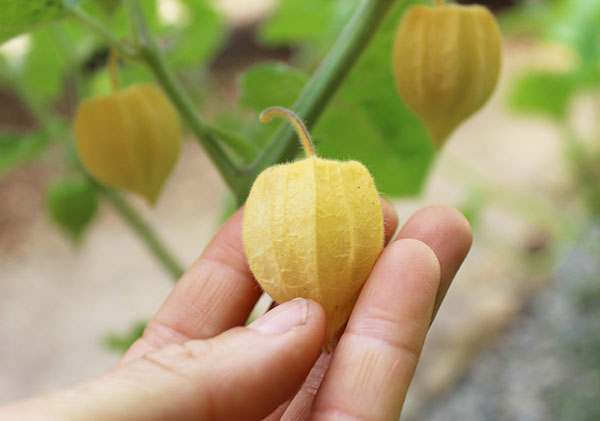

Grow Your Own Golden Berry Plant
Although the dried berries are mildly sweet, tart and quite tasty to snack on or use in various dessert recipes, there is nothing quite like the experience of eating a freshly picked ripe golden berry. They are a truly amazing taste sensation, gift wrapped in their own special papery package.
Fortunately, Physalis peruviana is very easy to propagate from viable seeds and will grow in many temperate climate zones, especially those with warmer summer seasons.
The golden berry plant itself is a low growing shrub with soft velvety leaves and requires full sun. It will grow plump ripe fruit with many berries coming in mostly in the summer season when warm to hot temperatures persist. This includes most all tropical locations as well as parts of California, Oregon, Florida and the Southern U.S. The berries grow best at higher altitudes where there is some fluctuation between night and day time temperatures.
The seeds can be started in the spring and transplanted into garden spaces in the early summer months. The golden berry plant, having a fairly shallow root system, also grows well as a potted plant, usually requiring at least a 10-20 gallon size container to thrive and produce a good yield of berries.
You can try to grow the plant from the raw dried berry seeds or seed packets can also be purchased.
Plants will lose their leaves and go dormant during colder seasons or frosts, but will come back the following spring with new growth. It does not tolerate snow pack or temperatures that much below freezing and will often die under such conditions.
As mentioned, golden berries when harvested can be eaten fresh or immediately dried for long term storage. This can be achieved using a food dehydrator, preferably on a low temperature setting below 115°F or 46°C to preserve nutritional quality.
We always encourage you to grow your own superfoods whenever possible. Not only do you get to consume the fresh homegrown end result, you also get to develop a special relationship with the plants and their natural cycle of life, which can be a very rewarding experience.

Health Benefits of Golden Berries
Contains Unique Plant Compounds Called Withanolides
One of the main compounds found in the berries and other parts of the golden berry plant are a group of naturally occurring phytochemical constituents that come from the nightshade family, referred to as "withanolides." Withanolides like withaferin A and withanone, were first isolated from the Ayurvedic herb, ashwagandha, and identified for their health enhancing attributes as immune system modulators, anti-inflammatories and tumor inhibiting agents. (Source)
The golden berry plant, especially the berries and roots, contain valuable amounts of withanolide glycosides such as the recently researched "4ß-hydroxywithanolide." Scientific evidence conducted on 4ß-hydroxywithanolide using isolates from Physalis peruviana berries, validates its ability to selectively kill oral cancer cells which may be a helpful adjunct during chemoprevention and related cancer therapies.
In 2013 research analysis it was stated that "this study showed, for the first time, that 4ßHWE (4ß-hydroxywithanolide) treatment selectively kills oral cancer cells in preference to normal oral cells. Further study of the target candidates and signaling mechanisms reported here may also provide a sufficiently improved understanding of the selective killing mechanisms of 4ßHWE to enable its effective use in treating oral cancer with minimal adverse effects."
In another study, published in the journal BioMed Central, extracts of
the fruit demonstrated anti-hepatoma and anti-inflammatory activities
and was shown to be a "chemotherapeutic agent against lung cancer." In
the same study it states that "golden berry-derived 4ßHWE may be a
promising ingredient as a cancer-preventive functional food."
In a 2014 animal experiment, golden berry extracts and to some degree the ripe fruits were shown to protect against liver (hepatic cell) damage.
Two separate studies published in the March 2013 and Dec 2013 Journal of Dietary Supplements, it was observed that both the golden berry juice and golden berry root extract with its "presence of alkaloids, withanolides and flavonoids", "succeeded in protecting the liver and kidney against fibrosis."
According to more research published in the 2014 journal, Planta Medica, "Physalis peruviana is a native plant from the South American Andes and is widely used in traditional Colombian medicine as an anti-inflammatory medicinal plant, specifically the leaves, calyces, and small stems in poultice form." In the study reported it was demonstrated that sucrose esters derived from P. peruviana "showed a potent anti-inflammatory effect."

High in Antioxidants, Vitamin C and Carotenoids
Along with other super berries, like camu camu, acai and maqui berry, golden berries are also a good source of vitamin C, a needed nutrient for collagen synthesis which is beneficial for healthy skin, bones and joints. Adequate levels of vitamin C consumed throughout the day, additionally help to boost cognitive and immune functions.
We highly recommend the use of whole plant-based vitamin C options over synthetically created ascorbic acid or "sodium ascorbate" supplements. Ascorbic acid isolate is a highly unstable substance and a pro-oxidant (the opposite of antioxidant) when used in high doses on a continuous basis. It is known to break down into oxalates, which can lead to oxalate stone formation as well as cause numerous health related problems. In a published 2015 study it was shown that "high-dose and low-dose vitamin C supplementation (or ascorbic acid) has been shown to cause secondary calcium oxalate nephropathy", or kidney stones.
Natural vitamin C is a complete and complex matrix of many different natural nutrients and compounds including enzymes, bioflavonoids and unique co-factors that help us absorb and effectively utilize ascorbic acid without causing harmful build-up in the body.
Good for the Eyes
Golden berries are high in carotenoid content and, like other members of the genus Physalis, are specifically rich in cryptoxanthin, a carotenoid that comes from the class of yellow-pigmented xanthophylls. Cryptoxanthin converts to vitamin A, a needed nutrient for the retina of the eye and provides antioxidant activity helpful for eliminating oxidative stress on ocular functions.
Likewise, the anti-inflammatory effects of Physalis peruviana fruit juice has been used as a folk remedy for treating benign eye growths in traditional South American medicine. (*)
Other Golden Berry Benefits
Golden berry fruit is a dietary source of melatonin, a hormonal substance good for providing a sound night's sleep and is believed to reduce the risk of neurodegenerative diseases associated with aging. (*)
The fruit moreover contains polyphenolic flavonoid compounds, like quercetin and kaempferol, that act as strong antioxidants and free radical scavengers. (*)
Golden Berry Nutrition
Golden berries or groundcherries are comprised of higher amounts of protein compared to other fruits.
According to Sunfood Superfoods, a 28 g serving of their dried golden berries contains 2 g protein, in addition to 30% of the Recommended Daily Value for vitamin A, 17% for potassium, 10% for vitamin C and manganese, 7% for magnesium, 6% for iron, 6% phosphorus, 4% for niacin, plus trace amounts of other vitamins and minerals.
The berries are additionally a low sugar, low calorie fruit with ample amounts of pectin content, a form of soluble fiber helpful for improving digestion and normalizing bowel movements as well as reducing LDL cholesterol levels.


Types of Golden Berry
Dried Berries - Golden berry is currently commercially available almost exclusively around the world as a whole dried fruit. Organic, low-temp sun-dried ripe berries are our recommended choice over other lower quality products. Dried golden berries have an inconsistent coloring, ranging from gold-brown to dark brown depending on the degree of ripeness. They are naturally a lighter color on the end of the berry where the fruit was attached to the papery calyx.
Whole Fresh Berries - The fruit, of course, can usually be found fresh in markets in tropical locations around the world. As mentioned, the berries can also be homegrown in many other temperate climate zones and will thrive in most garden spaces or permaculture settings.
How to Use
Golden berries, with their sweet and tart flavor, go very well in many raw dessert recipes, especially vegan cheesecakes, pies and lemon bars. They can also be blended up with other superfruits into protein shakes, smoothies, kefir, lemonade and are an extra special ingredient in one of our raw chocolate recipes. They are commonly used around the world in jams, sauces and puddings.
The dried berries also make a delicious snack food incorporated into trail mixes or can be eaten like raisins. When using dried versions in recipes it is often helpful to soak them first before processing.
Precautions:
While the golden berry plant and its fruits are generally considered non-toxic, excessively high doses especially when concentrated as a fruit juice may result in a number of toxic side-effects. The berries should be avoided by those with allergies or sensitivity to foods from the nightshade family.
Shop Related Products (About Affiliates & Amazon Associate Paid Links)
Affiliate Disclaimer: This section contains affiliate product links. If you make a purchase through our recommended links, we receive a small commission at no additional cost to you. Thanks for the support.